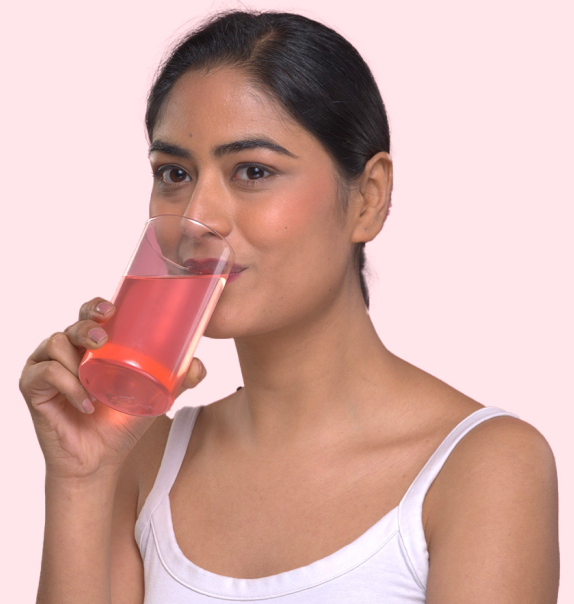
Our No List
Sugar

Nuts
Soy
GMO
Gluten

Diary
Baking Soda
Lactose
Certifications



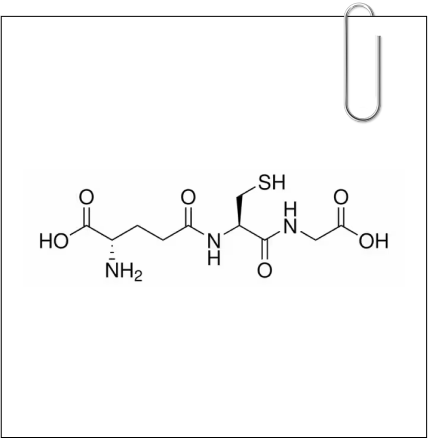
Glutathione:
Glutathione, a potent antioxidant, is widely employed in dermatology for skin brightening and lightening. Its versatility allows for oral, intravenous, and topical applications. Often hailed as the "Wonder drug" for hyperpigmentation, it plays a crucial role in building cell health. Discovered in 1888, its name comes from its composition of cysteine, glutamate, and glycine. Initially used for various conditions, its unexpected positive impact on skin tone led to widespread use in dermatology. Research highlights its antioxidative properties and importance in nutrient metabolism.1
Glutathione, a potent antioxidant, is widely employed in dermatology for skin brightening and lightening. Its versatility allows for oral, intravenous, and topical applications. Often hailed as the "Wonder drug" for hyperpigmentation, it plays a crucial role in building cell health.
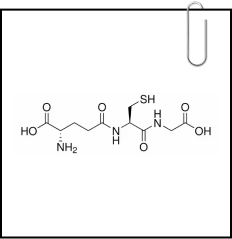 Discovered in 1888, its name comes from its composition of cysteine, glutamate, and glycine. Initially used for various conditions, its unexpected positive impact on skin tone led to widespread use in dermatology. Research highlights its antioxidative properties and importance in nutrient metabolism.1
Discovered in 1888, its name comes from its composition of cysteine, glutamate, and glycine. Initially used for various conditions, its unexpected positive impact on skin tone led to widespread use in dermatology. Research highlights its antioxidative properties and importance in nutrient metabolism.1
Do you know? Your body naturally produces glutathione but in a very small portion, but you can also get it from foods like spinach, avocado, and mushrooms. Whey protein is another rich source. These foods provide essential building blocks for your body to make glutathione.2
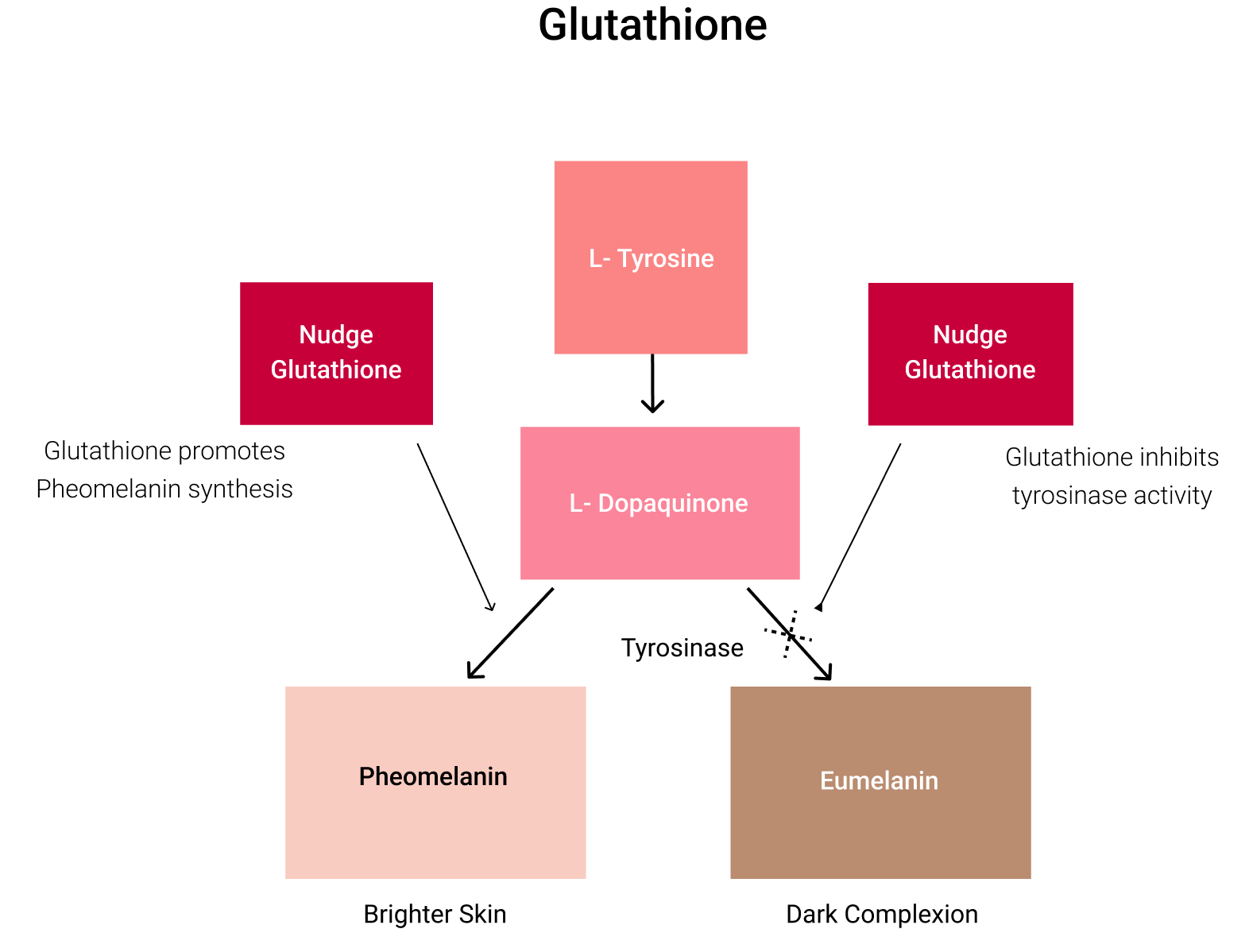
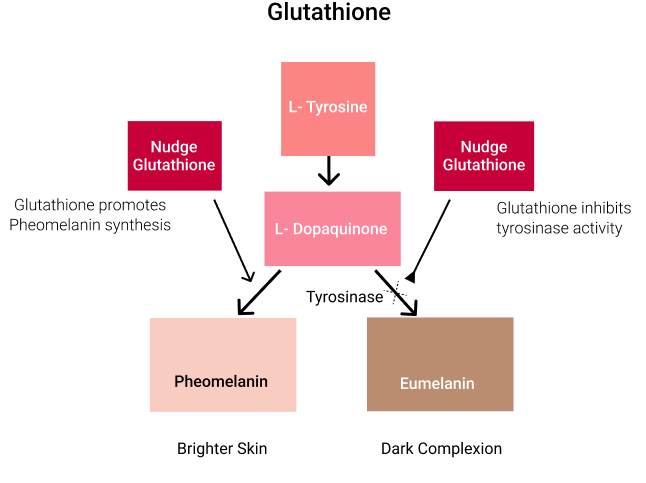
How does Gutathione work?
- Direct inactivation of the enzyme “tyrosinase”
- Switching off the production of the Eumelanin (gives darker complexion)
- Switching on the production of the Pheomelanin (gives brighter complexion)
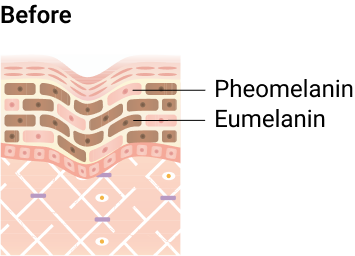
Sun exposure and oxidative stress can disrupt melanin levels, leading to an increase in Eumelanin for a darker complexion, and a decrease in Pheomelanin, resulting in a brighter tone.
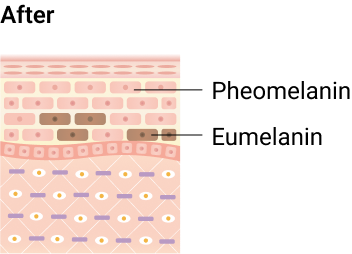
Glutathione aids in balancing melanin production by partially deactivating the tyrosinase enzyme. This process turns off Eumelanin production and turns on Pheomelanin production, promoting a younger and radiant skin appearance.
What benefits Glutathione give me?
- Improves skin tone: Glutathione boosts the production of pheomelanin, to give brighter skin tone. It influences enzymes, to limits tyrosinase, and eumelanin. In clinical studies, Glutathione outperformed a 2% Hydroquinone cream, significantly reducing the skin's melanin index.1,2,3
- Antioxidant Properties: Glutathione helps protect your skin from damage caused by UV rays and environmental stressors. It neutralizes harmful free radicals that can lead to issues like wrinkles and inflammation.1,2,3
- Anti-Aging: Glutathione boosts collagen production, reducing wrinkles and improving skin moisture. Younger individuals can apply it topically in their skincare routine. For older individuals, both oral and topical use can harness its anti-aging and anti-pigmentation benefits.1,2,3
Clinical significance of glutathione
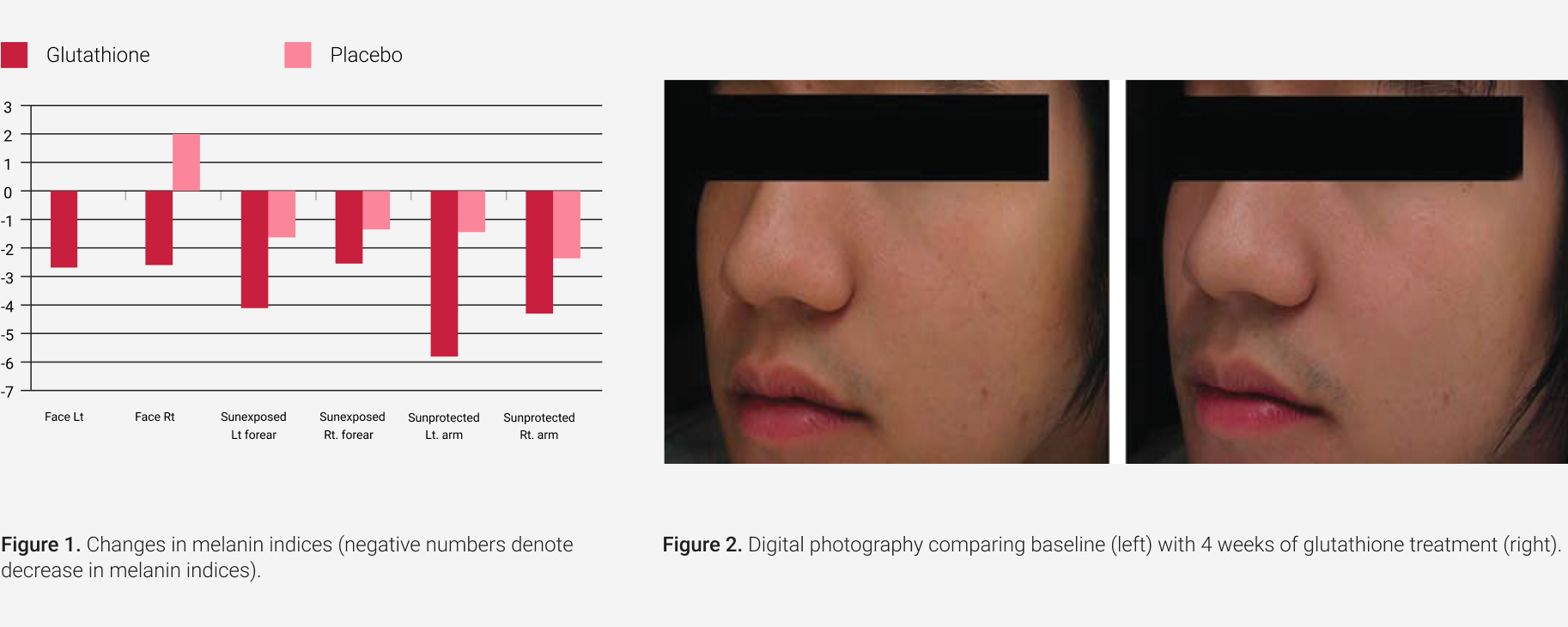
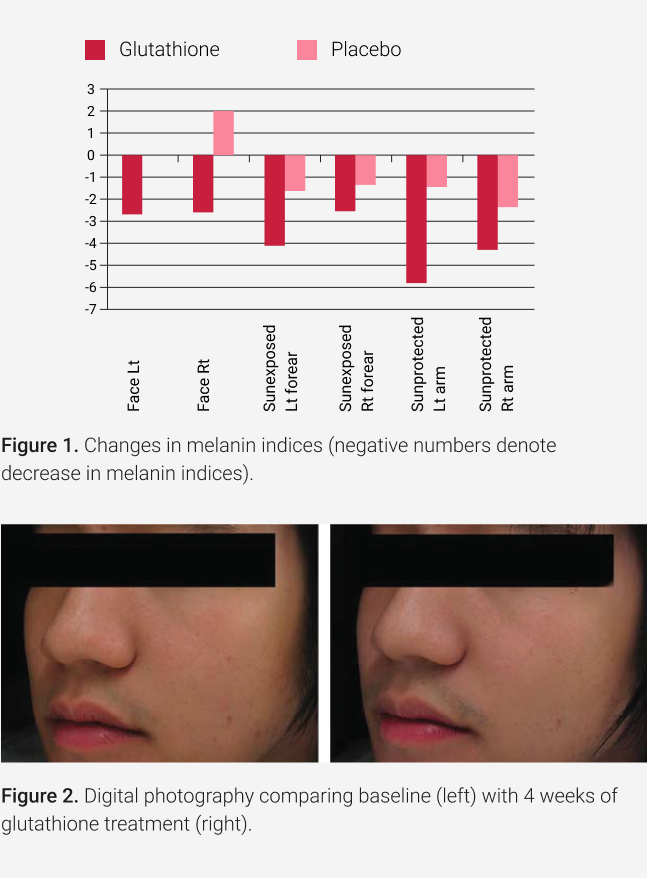
- Study-1: Published in Journal of dermatological treatment11
- Summary: In a 4-week trial with 60 participants, those using glutathione experienced consistent melanin index reduction across all six sites. Statistically significant decreases were noted, particularly on the right side of the face and the sun-exposed left forearm, when compared to the placebo group.
- Conclusion: Oral glutathione administration results in a lightening of skin Color in a small number of subjects.
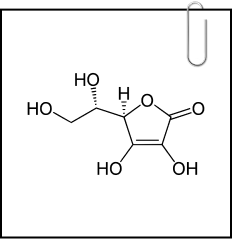
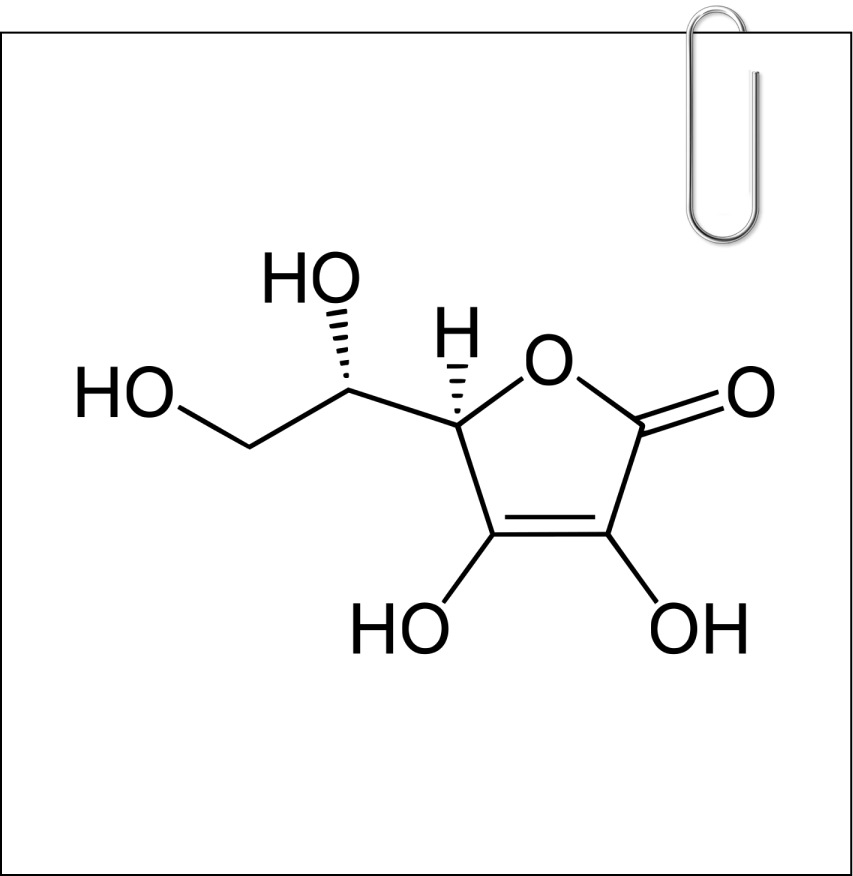
Hyaluronic acid:
A natural occurring water loving molecule helps plump, smooth and moisturize the skin from inside to give you never ending natural glowing skin*. It optimizes the absorption and improve the skin hydration from within*.Hyaluronic also known as hyaluronan or hyaluronate —a natural gooey, glassy substance in your body, is vital for skin hydration, swelling, and structural support, especially in eyes, joints, and skin. Aging leads to reduced hyaluronic acid and collagen, causing skin elasticity loss and the formation of wrinkles.7
A natural occurring water loving molecule helps plump, smooth and moisturize the skin from inside to give you never ending natural glowing skin*. It optimizes the absorption and improve the skin hydration from within*.
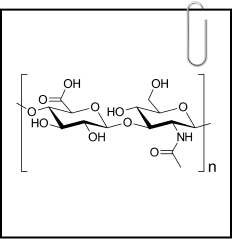
Hyaluronic also known as hyaluronan or hyaluronate —a natural gooey, glassy substance in your body, is vital for skin hydration, swelling, and structural support, especially in eyes, joints, and skin. Aging leads to reduced hyaluronic acid and collagen, causing skin elasticity loss and the formation of wrinkles.77
How does Hyaluronic acid work?23
- Hyaluronic acid attracts and holds water, adding volume and structural support to the skin.
- Aging reduces natural hyaluronic acid and collagen production, leading to wrinkles.
- Supplementation with hyaluronic acid replenish lost volume, reducing the appearance of wrinkles.
- They also stimulate collagen production and impact fibroblast morphology, countering the effects of aging.
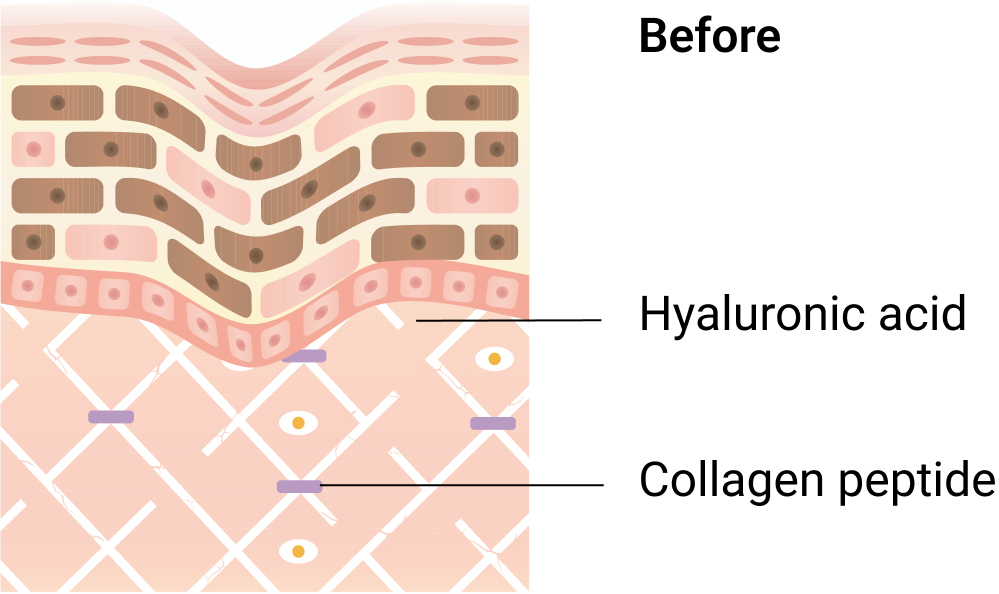
The aging process, coupled with oxidative stress, diminishes hyaluronic acid and collagen peptide levels. This reduction leads to the development of wrinkles, dry skin, and early signs of aging, even in one's 20s.
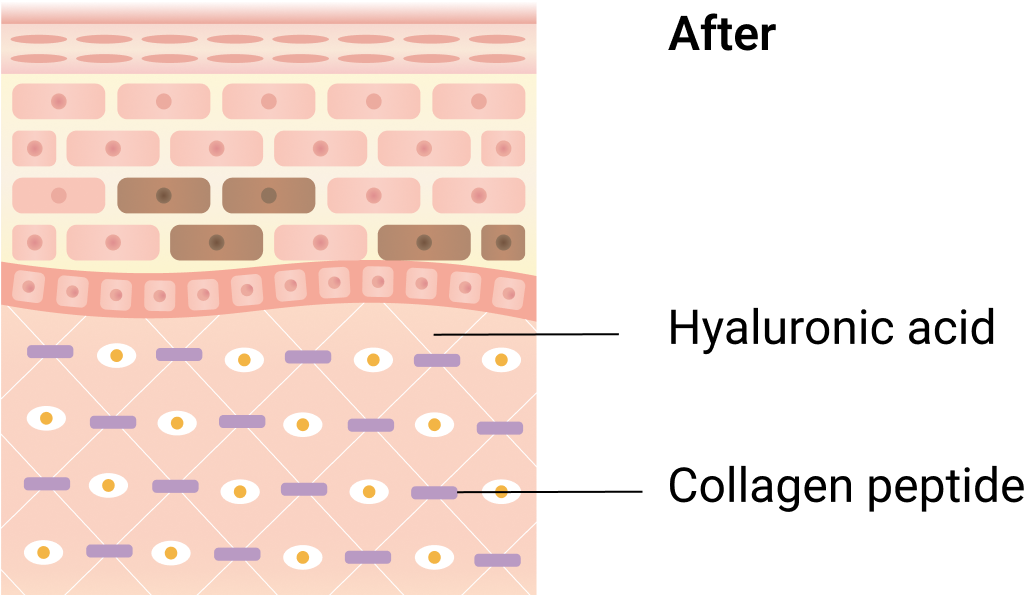
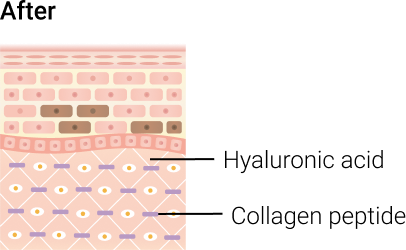
Supplementation of hyaluronic acid levels through supplementation facilitates water absorption into the skin and stimulates collagen production, resulting in a smoother and wrinkle-free complexion.
What benefits Hyaluronic acid give me?7
- Reduces wrinkles: It provides a gel to the skin that attracts water, creating structural support and aiding in the reduction of wrinkles
- Improves skin elasticity: As hyaluronic acid acts a water lover molecule. It helps in enhance skin elasticity.
- Improves collagen level: it helps in providing the favourable environment of well hydrated skin for better collagen production
Clinical significance of glutathione6
- In 2017, two studies were conducted.
- A blend of Hyaluronic acid, Zinc, and Vitamin C was found to enhance skin hydration, elasticity, and reduce wrinkles within a 20 to 40 days intake period.
- Additionally, a 12-week study showed that a daily dosage of 120 mg of Hyaluronic acid contributed to improved skin condition and reduced wrinkles compared to a placebo6
Vitamin C:
Naturally derived extract helps to improve the collagen formation, reduce skin aging, wrinkles and improve skin glow through reducing oxidative stress.
Naturally derived plant-based vitamin C made with acerola plant extract which is easy to recognize to body and use*. It helps in protect your body from oxidative stress and supports natural skin. It also helps in production of the collagen8. Natural vitamin C has better absorption than other form of vitamin C according to recent study.9
Clinical significance of Vitamin C10
- In 2007, Cosgrove et al conducted a study to assess the associations between nutrient intake and skin aging in more than 4000 women aged 40 to 74 years.
- Higher dietary vitamin C intakes were associated with a significantly lower likelihood of senile xerosis and wrinkled appearance (P<.009). Role of vitamin C in skin are promotion of collagen formation, inhibition of melanogenesis, reduce skin aging and wrinkles.10

Reel Vs Reality
The expectations and outcomes of using glutathione supplements and topical creams for achieving bright and clear skin can differ between the reel (perceived or portrayed) and reality. It's important to have a realistic understanding of what these products can and cannot achieve.
Reel Vs Reality
The expectations and outcomes of using glutathione supplements and topical creams for achieving bright and clear skin can differ between the reel (perceived or portrayed) and reality. It's important to have a realistic understanding of what these products can and cannot achieve.
| Reel | Reality |
|---|---|
| Quick & dramatic results | |
| Ads suggest that using glutathione supplements or creams leads to instant and dramatic skin transformation. | Not so fast! Visible changes take time, as skin regeneration is a gradual process, requiring consistent use. |
| Uniform skin tone | |
| Products promise a flawlessly even skin tone, erasing all blemishes and discolorations. | Improvement is likely, but perfect uniformity is rare due to factors like genetics and sun exposure. |
| Flawless complexion | |
| Ads showcase people achieving flawless, airbrushed skin with glutathione products. | Flawless skin is a challenge, and individual results vary. Improvement is the goal, not perfection. |
Nudge Glutathione Performance

Day 0

Day 30
Reduced blemishes, dark spots,
and uneven skin tone

Day 60
Brightened and
glowing skin

Day 90
See clear
skin!
Wondering “why we didn't create our product in effervescent form?”
Do you know that most effervescent tablets contain sodium bicarbonate, also known as baking soda or INS 500 (ii), to create fizz in drinks, providing a pleasant sensation? However, this fizzy effect can lead to unintended issues in your body.
Let's break down how much baking soda/INS 500 (ii) is typically found in one effervescent tablet.
On average, a 4-gram effervescent tablet contains about 1 to 2 grams of baking soda/INS 500 (ii).
According to safety data sheets and federal standards, the lethal dose (L50) of baking soda is 2000 – 5000 mg/kg12, which can cause mild to severe side effects, including stomach issues13, interference with medication15, dryness and aging skin, metabolic alkalosis13, and hypernatremia14.
| Issue | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Stomach discomfort | The effervescent reaction in the stomach can cause discomfort for some individuals, particularly those with sensitive digestive systems.18
Global ratings of gastrointestinal distress severity (0-10 scale) were greater after bicarbonate ingestion21 |
| Gas & bloating | Effervescent drugs can release carbon dioxide gas when dissolved in water, leading to gas and bloating in some individuals.19 |
| Tooth erosion | The acidic nature of effervescent tablets can potentially contribute to tooth erosion over time, especially if they are frequently consumed.19 |
| Allergic reactions | Some individuals may be allergic to certain ingredients in effervescent drugs, leading to allergic reactions such as hives, itching, or swelling.19 |
| Electrolyte imbalance | Effervescent drugs containing high levels of certain electrolytes, such as sodium or potassium, may lead to imbalances in the body's electrolyte levels.19 |
| Excess urination | Consuming baking soda can cause a variety of side effects. If people ingest baking soda, they will need to urinate more because of the loss of essential electrolytes20 |
| Kidney issues | Too much baking soda can impair kidneys work, potentially preventing the kidneys from filtering out the baking soda properly.20 |
| Diarrhea & nausea | 10 of the 11 subjects (91%) experienced diarrhea, 64% experience bloating and thirst, and 45% experienced nausea after bicarbonate loading.21 |
| Acidic burps | The increase in pH caused by sodium bicarbonate can also affect the balance of stomach acid, potentially leading to acid reflux.22 |
- Considering the long-term regime of glutathione, along with pros and cons of effervescent formulations, we made a conscious decision to build our new formulation from scratch. Keeping in line with the Nudge promise of "clean, transparent, and science," we introduced Nudge Glutathione to help you achieve clear and healthy skin in just 90 days.
How Nudge glutathione is different?
| Nudge Glutathione (Powder form) |
Glutathione (Effervescent tablet form) |
|---|---|
| Percentage of Active and inactive ingredients: 84% and 16% | Percentage of Active and inactive ingredients: 60% and 40%* *: may vary according to the formulations |
| Contains sucralose (non-calorie sugar) | Contains sugar such as polysaccharides- Dextrose, Maltodextrin |
| Contains L-Glutathione for faster absorption in the body | Contains regular Glutathione with slower absorption in the body |
| No baking soda, No bloating | May cause bloating due to excess amount sodium bicarbonate |
| Easy to dissolve and quickly soluble | Slow dissolving time- around 2 minutes |
| Economical | High Price |
| In blueberry flavour- feel natural taste | Unpleasant due to fizz and metallic taste |
References:
- Li, Y., Wei, G., & Chen, J. (2004). Glutathione: a review on biotechnological production. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 66, 233-242.
- Watanabe, F., Hashizume, E., Chan, G. P., & Kamimura, A. (2014). Skin-whitening and skin-condition-improving effects of topical oxidized glutathione: a double-blind and placebo-controlled clinical trial in healthy women. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 267-274.
- Allen, J., & Bradley, R. D. (2011). Effects of oral glutathione supplementation on systemic oxidative stress biomarkers in human volunteers. The journal of alternative and complementary medicine, 17(9), 827-833.
- Matuz-Mares, D., Riveros-Rosas, H., Vilchis-Landeros, M. M., & Vázquez-Meza, H. (2021). Glutathione participation in the prevention of cardiovascular diseases. Antioxidants, 10(8), 1220.
- Malathi, M., & Thappa, D. M. (2013). Systemic skin whitening/lightening agents: what is the evidence?. Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology, 79, 842.
- Oe, M., Sakai, S., Yoshida, H., Okado, N., Kaneda, H., Masuda, Y., & Urushibata, O. (2017). Oral hyaluronan relieves wrinkles: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled study over a 12-week period. Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology, 267-273.
- Göllner, I., Voss, W., von Hehn, U., & Kammerer, S. (2017). Ingestion of an oral hyaluronan solution improves skin hydration, wrinkle reduction, elasticity, and skin roughness: Results of a clinical study. Journal of evidence-based complementary & alternative medicine, 22(4), 816-823.
- Kishimoto, Y., Saito, N., Kurita, K., Shimokado, K., Maruyama, N., & Ishigami, A. (2013). Ascorbic acid enhances the expression of type 1 and type 4 collagen and SVCT2 in cultured human skin fibroblasts. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 430(2), 579-584.
- Uchida, E., Kondo, Y., Amano, A., Aizawa, S., Hanamura, T., Aoki, H., ... & Ishigami, A. (2011). Absorption and excretion of ascorbic acid alone and in acerola (Malpighia emarginata) juice: comparison in healthy Japanese subjects. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 34(11), 1744-1747.
- Pullar, J. M., Carr, A. C., & Vissers, M. (2017). The roles of vitamin C in skin health. Nutrients, 9(8), 866.
- Arjinpathana, N., & Asawanonda, P. (2012). Glutathione as an oral whitening agent: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Journal of dermatological treatment, 23(2), 97-102.
- Cat. # RC-092 - G-biosciences. (n.d.). https://cdn.gbiosciences.com/pdfs/msds/RC-092_msds.pdf
- Thomas, S. H., & Stone, C. K. (1994). Acute toxicity from baking soda ingestion. The American journal of emergency medicine, 12(1), 57-59.
- Kupiec TC, Goldenring JM, Raj V. A non-fatal case of sodium toxicity. J Anal Toxicol. 2004 Sep;28(6):526-8. doi: 10.1093/jat/28.6.526. PMID: 15516309.
- Baking soda for heartburn. Gastrointestinal Society. (2020, July 14). https://badgut.org/information-centre/a-z-digestive-topics/baking-soda-for-heartburn/
- Grgic, J., Rodriguez, R. F., Garofolini, A., Saunders, B., Bishop, D. J., Schoenfeld, B. J., & Pedisic, Z. (2020). Effects of sodium bicarbonate supplementation on muscular strength and endurance: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Medicine, 50, 1361-1375.
- Freis, T., Hecksteden, A., Such, U., & Meyer, T. (2017). Effect of sodium bicarbonate on prolonged running performance: A randomized, double-blind, cross-over study. PloS one, 12(8), e0182158.
- Ipci, K., Öktemer, T., Birdane, L., Altintoprak, N., Muluk, N. B., Passali, D., ... & Cingi, C. (2016). Effervescent tablets: a safe and practical delivery system for drug administration. ENT updates, 6(1), 46.
- Perrin, G., Berdot, S., Thomas, F., Pannier, B., Danchin, N., Durieux, P., & Sabatier, B. (2018). Evaluation of exposure to effervescent drugs in a large health check-up population in France: a cross-sectional study. BMJ open, 8(7).
- Hughes, A., Brown, A., & Valento, M. (2016). Hemorrhagic encephalopathy from acute baking soda ingestion. Western Journal of Emergency Medicine, 17(5), 619.
- Kahle, L. E., Kelly, P. V., Eliot, K. A., & Weiss, E. P. (2013). Acute sodium bicarbonate loading has negligible effects on resting and exercise blood pressure but causes gastrointestinal distress. Nutrition Research, 33(6), 479-486.
- Carr, A. J., Slater, G. J., Gore, C. J., Dawson, B., & Burke, L. M. (2011). Effect of sodium bicarbonate on [HCO3−], pH, and gastrointestinal symptoms. International journal of sport nutrition and exercise metabolism, 21(3), 189-194.
- Walker, K., Basehore, B. M., Goyal, A., & Zito, P. M. (2018). Hyaluronic acid.







